MPS
# Construct models that mimic living organisms to improve the accuracy of compound evaluation.
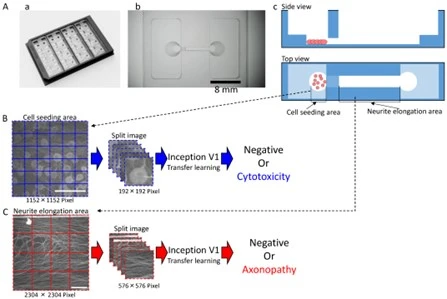
Using microfluidic devices, we construct models suitable for compound evaluation and heterogeneous cell binding models that mimic living organisms to evaluate compounds in a high-throughput manner. AI analysis and multivariate analysis of measured data (images) are used to predict the toxicity, efficacy, and mechanism of action of compounds. Biomarker assay is also performed in combination as needed.
(Jointly developed with USHIO Inc.)
Reference papers (excerpts)
X. Han, N. Matsuda, M. Yamanaka, I Suzuki*, Development of a Novel Microphysiological System for Peripheral Neurotoxicity Prediction Using Human iPSC-Derived Neurons with Morphological Deep Learning, Toxics, 12(11), 809, 2024 DOI
K. Matsuda, X Han, N. Matsuda, M. Yamanaka, I Suzuki*, Development of an In Vitro Assessment Method for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN) by Integrating a Microphysiological System (MPS) with Morphological Deep Learning of Soma and Axonal Images, Toxics 11(10) 848, 2023 DOI
X Han, N Matsuda, K Matsuda, M Yamanaka, I Suzuki*, “An in vitro microfluidic culture device for peripheral neurotoxicity prediction at low concentrations based on deep learning” Fundam. Toxicol Sci., Vol. 9 No. 7 pp. 203-209, 2022 DOI
Odawara, A., Gotoh, M., and Suzuki, I.* “A three-dimensional neuronal culture technique that controls the direction of neurite elongation and the position of soma to mimic the layered structure of the brain” RSC Advances 3(45) (2013) pp. 23620-23630. DOI
Odawara, A., Gotoh, M., and Suzuki, I.* “Control of neural network patterning using collagen gel photothermal etching,”Lab on a chip 13 (2013), pp.2040-2046. DOI
Suzuki, I.*, Nakamura, K., Odawara, A., Alhebshi, A., Gotoh, M., “A simplified micropatterning method for straight-line neurite extension of cultured hippocampal neurons,” Analytical Sciences, 29(2), (2013),263-266 DOI